Nursing care plans are a significant factor in the learning of both students in this field and healthcare professionals. These care plans are not just any ordinary documents; rather, they are the sole source and foundation upon which the quality of patient care stands. It documents every aspect of patient care, medication, and interventions. What the patient is undergoing, how it will be addressed, and what the progress milestone should be, nursing students and professionals document all of these factors in the care plans.
In the healthcare field, particularly nursing, a well-updated care plan is not just about diagnosing and medication strategies. It is a clear and effective source of communication among healthcare staff as well. In case of nursing shift change or sharing expertise for better patient care, these plans are treated as a reliable source of information.
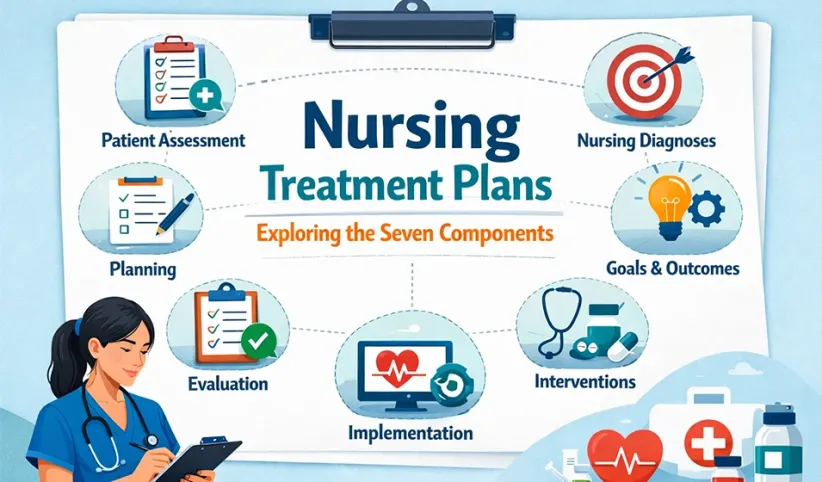
Nursing Care Plan Format
There are various types and different formats for nursing care plans. In some cases, it is only based on three sections, including;
- Nursing diagnosis
- Outcomes and evaluation
- Interventions
Whereas in other cases, it is written in five-column format, such as;
- Assessment
- Diagnosis
- Outcomes
- Interventions
- Rationales
- evaluation
Care Plans and Students' Learning
Given the significance of these care plans, nursing students must be well-trained and equipped with the knowledge and skills to develop care plans effectively during their studies. This will not only facilitate professional development but will also enhance their critical thinking, patient-focused care, understanding of individualised needs of patients, and how to align their practices with ethical guidelines and the best clinical practices.
However, considering academic challenges, clinical placements, and research complexities, nursing students often fail to develop their care plan assignments based on the guidelines. They lack the knowledge to include or avoid aspects that can easily affect their grades. This is why we are offering the top Do’s and Don’ts here so that students can better prepare their care planning assignments and leverage the required skills and learning.
The Top Do’s of Developing Care Plans
Follow the Nursing Process (ADPIE)
A written and well-organised nursing care plan makes all the difference. Hence, always structure your care planning assignment based on the standard format, such as (ADPIE) Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning, Implementation, and Evaluation.
Use Nursing Diagnoses, Not Medical Ones
Always use nursing diagnosis instead of the medical one to describe the patient's condition. For example, ineffective airway clearance due to mucus buildup, etc, will be used instead of Pneumonia when describing the condition of the patient. This better helps nurses to suggest tailored care solutions independently.
Set SMART Goals
When you list down goals for patient progress, ensure that you are formulating practical ones reflecting Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and Time-bound outcomes.
For example, if the patient has an acute pain nursing diagnosis, the SMART goal would be “Patient will report pain level ≤3/10 within 1 hour of medication.”
Base Plans on Real Data
Prepare fact-based care planning assignments instead of guesses or opinions, as it can impact your professional credibility later in the practical field. Hence, always comprehensively write the patient assessment column, covering all aspects of the patient’s condition, and formulate your care plan based on that data only.
Choose Evidence-Based Interventions
Always offer nursing interventions based on strong evidence. Plus, it must be well aligned with ethical and most effective clinical practices. Your nursing actions should be supported by rationale in light of current and credible field research.
The Top Don’ts of Nursing Care Plans
Don’t Use Vague Goals
When writing goals and outcomes, nursing students often use vague writing, such as “the patient will feel better”. Avoid doing that; instead, be specific and focused.
Don’t Skip Steps
Follow the proper format of the nursing care plan as suggested by your institute. Jumping from diagnosis to intervention or leaving out evaluation may impact your professional learning. Plus, it can also cost you grades.
Do Not Copy and Paste Templates
Never rely on templates solely. They are helpful, and you can use them for efficient work. However, always customise them according to your specific patient scenario. If you want to use template-based care plans, you can get them from professional help with nursing assignments UK services. These services offer customised and professional care plan templates prepared by nursing specialists.
Don’t Use Personal Opinions or Informal Language
Do not use language in your care plan writing beyond what academic standards dictate. Always write in a clear, fact-based, objective, and formal manner. Vague phrases, guesswork, or lack of evidence can impact the credibility of your nursing expertise.
Don’t Forget to Prioritise
As a nurse, you must deal with patients experiencing various health issues. Hence, when crafting a care plan, train your mind to focus on the most important problems first. For example, if a person is facing these conditions: Pain level 8/10, shortness of breath, and mild anxiety. You should first look into shortness of breath as it is life-threatening, followed by pain as it is a serious discomfort, and then anxiety. Students can also use Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs or the ABCs for better conduct in this situation.
Conclusion
Nursing care plans are central to patient-focused care and providing practical nursing expertise to students. Hence, they should not be treated as any other academic documents, but must be formulated with standard compliance and well-researched insights. From following the structural requirements of these nursing assignments to ensuring strong and reliable evidence for nursing interventions, students have to focus on all aspects of this document to produce a well-communicated, fact-based, and comprehensive care manual that could contribute to patient safety and health and reflect the nursing proficiency of students.